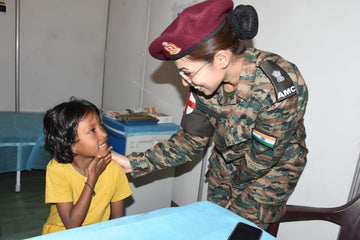
The Indian Army is not only recognized for its strategic might and discipline but also for its commitment to the health and wellness of its personnel. At the forefront of this commitment are the Medical Officers. These medical professionals play a pivotal role in ensuring the health and operational readiness of soldiers, making their roles essential to the functioning of the Army. In this article, we delve into the salary, eligibility criteria, and educational qualifications required to become a Medical Officer in the Indian Army.
Historical Context
The roots of military medicine in India trace back to ancient times, where healers and physicians served the warriors. However, modern military medical service began to take shape during British colonial rule, with the establishment of several medical corps. The Indian Army Medical Corps (AMC) was formed in 1943, marking a significant evolution in the organization and specialization of military medical services. Over the decades, the roles and responsibilities of military medical officers have expanded, adapting to the changing nature of conflicts and advancements in medical science.
Educational Qualifications
To become a Medical Officer in the Indian Army, candidates typically pursue one of two primary routes: through the Armed Forces Medical College (AFMC) or through the Army Medical Corps (AMC).
Through the Armed Forces Medical College (AFMC)
-
Eligibility Requirements
- Candidates must first clear the National Eligibility cum Entrance Test (NEET) to gain admission into AFMC.
- Following successful NEET results, candidates undergo a Service Selection Board (SSB) interview and a comprehensive medical examination to assess their fitness for military service.
-
Training and Commissioning
- Upon successful admission, candidates embark on a rigorous 5.5-year MBBS program, integrating both theoretical knowledge and practical training.
- Graduates receive a permanent commission as Medical Officers upon completion of their course, allowing them to serve in various capacities throughout the Army.
Through the Army Medical Corps (AMC)
-
Eligibility Requirements
- Candidates should possess an MBBS or BDS degree from a recognized medical institution. For Dental Officers, a BDS with at least 60% marks in the final year or an MDS from a recognized college is required, along with completion of a one-year rotatory internship.
- Those holding these qualifications may apply for a Short Service Commission (SSC), typically involving an initial commitment of ten years, which can be extended by another four years depending on performance and requirement.
-
Selection Process
- Similar to the AFMC route, AMC candidates undergo an interview and a medical examination to ensure they meet the requisite standards.
Eligibility Criteria
General Eligibility
To qualify for commission as a Medical Officer in the Indian Army, candidates must adhere to certain physical and medical standards, including:
- Height: Minimum requirement is 157.5 cm for males and 152 cm for females.
- Weight: Proportionality of weight to height must be maintained, ensuring individuals meet the Army's health standards.
Medical Examination
The medical examination is a comprehensive process that is essential in the selection regime. It checks various health parameters, including:
- X-ray examinations
- Blood tests
- Urine tests
Candidates may face temporary rejection due to issues like being underweight or overweight, while individuals with specific medical conditions may face disqualification from the process altogether.
Review Medical Board (RMB)
If a candidate believes their medical rejection was unwarranted, they have the option to appeal for a Review Medical Board (RMB), which reassesses their medical fitness.
Selection Process
The process of selection for Medical Officers varies depending on the chosen route for entry:
AFMC Route
- Clear the NEET exam.
- Undergo SSB interview.
- Complete medical examinations.
- Finish the 5.5-year MBBS program.
AMC Route
- Hold the requisite medical degree (MBBS or BDS).
- Attend an interview.
- Undergo medical examination.
- Serve under a short service commission with potential transition to a permanent commission.
Salary
The specific salary details for Indian Army Medical Officers are generally competitive, divided across multiple components:
- Basic Pay: Determined by the officer's rank and length of service.
-
Allowances: Medical Officers are entitled to several allowances, which typically include:
- Dearness Allowance: Adjusted based on the cost of living.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): Based on their posting location.
- Transport Allowance: Covers official and personal travel.
- Other Benefits: Medical Officers also receive other benefits such as free medical treatment for themselves and their families, access to facilities like canteens, and educational allowances for children.
Estimated Salary Range
While exact figures can vary based on rank and years of service, a newly commissioned Medical Officer may expect to start with a salary ranging from INR 70,000 to 90,000 per month, which can increase significantly with experience, specialization, and promotions.
Additional Considerations
Stringent Medical Standards
The Indian Army upholds rigorous standards to ensure all selected candidates can handle the physical and mental demands of military duty. This involves stringent criteria for vision (including color perception), body mass index (BMI), and overall health.
Continuous Professional Development
Medical Officers in the Indian Army have opportunities to further their education and skills through specialized training courses, workshops, and seminars, thus encouraging continuous professional growth.
Case Studies or Real-World Applications
Service and Contributions
Medical Officers in the Indian Army, such as those who served during the Kargil War in 1999, demonstrated not only medical expertise but also incredible courage and resilience. They provided essential medical support in difficult terrains and conditions, often managing complex injuries amid combat. Their contributions have not only saved lives but have also shaped military medical protocols for future conflicts.
Statistical Data and Research Insights
The relevance of mental health and well-being among military personnel has gained increasing recognition. According to research by Dr. B.L. Usmani, an expert in military medicine, stressed that military medical officers play a crucial role in addressing mental health issues. Approximately 20-30% of soldiers deployed in high-stress environments experience emotional and psychological challenges, leading to an emerging focus on mental health treatments in military medical training curricula.
Comparative Analysis
When comparing medical officers in the Indian Army with civilian counterparts, the differences in lifestyle, workload, and responsibilities become clear. While civilian doctors often work in more predictable environments with set hours, Army Medical Officers may be deployed in remote areas under challenging conditions without the luxuries of civilian medical practice. The camaraderie and teamwork within military units add a unique dimension to their service that is often unmatched in civilian settings.
Challenges and Solutions
Challenges
- High-stress Environment: Medical Officers often face high-pressure situations requiring rapid decision-making.
- Work-life Balance: Managing personal life and commitments while serving the Army can be demanding.
- Dealing with trauma: Officers must cope with handling traumatic injuries, which can lead to burnout or PTSD.
Proposed Solutions
- Mental Health Support: Implement regular counseling and mental health check-ins for medical personnel.
- Better Work Scheduling: Structure shifts to allow for sufficient downtime to help combat burnout.
- Support Groups: Create platforms for sharing experiences and challenges among medical officers to foster a strong support network.
Future Trends and Predictions
As healthcare technology evolves, the role of Medical Officers in the Indian Army will also adapt. Incorporating telemedicine and advanced medical technologies could significantly improve medical care in remote and battle situations. Additionally, increased awareness and strategy on mental health support within military medical education will ensure that future officers are better equipped to handle the psychological demands of their duties.
Conclusion
Becoming a Medical Officer in the Indian Army is both a prestigious and challenging career path. It requires rigorous educational qualifications, adherence to stringent eligibility criteria, and a commitment to serving the nation. As the medical field continues to evolve, candidates who aspire to this role must be prepared to embrace ongoing learning and adapt to new challenges.
The significance of medical officers goes beyond mere treatment; it encompasses a holistic approach to maintaining the health and readiness of one of the world's finest armies. For those who have the calling to combine medical expertise with national service, the Indian Army awaits—a place where skill meets duty, and dedication knows no bounds.
If you are inspired to tread this path, consider utilizing resources such as those offered by SSBCrack and SSBCrackExams, which provide comprehensive preparation tools and materials for aspiring candidates. The journey may be tough, but the reward of serving your nation as a Medical Officer makes it worthwhile.
If you have any questions or wish to share your thoughts on this topic, feel free to leave a comment below. Your input is invaluable in fostering a community of informed, future medical officers.